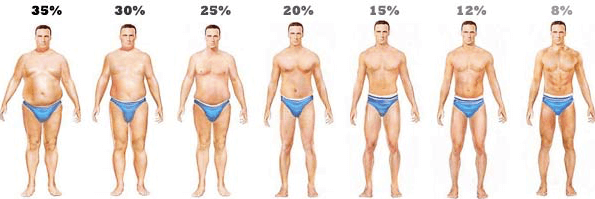
Well for what ever reason, you have found yourself a little over weight or your looking simply to get in better shape for your sport! There are many ways to help lose that weight and it all comes down to energy balance, we I have covered HERE
One of the elements around Energy balance is that of The Thermic Effect of Food, food that has a higher calorie cost when you eat and digest means that its not as simple as eating a 100 calorie snack if that snack costs you 50 calories to eat and digest!!! so lets take a look into that!
Each Food Macro has a different element of how much our bodies need to do when eating and digesting in order to break it down, we know that each Macro with provide you different amounts of Calories (Fat being the highest) but they also cost different to digest and with that each micro element of food has a difference in how much our body takes to digest which is the element of TEF – Thermic Effect Of Food
I’m gonna give your foods first, as that’s what you really want right? haha then if you want the science please keep reading the bottom of the article 🙂
Do They Help You Burn Fat?
There are a ton of supplements on the market in the realm of thermogenises, Here’s some of the research behind the most popular thermogenic compounds to determine if they actually help burn body fat.
What Are Thermogenic Supplements?
The word “thermogenic” literally means heat-producing.
When your body burns calories, it generates more heat, so supplements that boost metabolism or fat burning are considered thermogenic.
Many different types of these supplements are available over the counter.
Some contain just one ingredient, while others use a blend of metabolism-boosting compounds.
Manufacturers claim that these supplements will help you lose weight or burn more body fat, but the veracity of this claim is hotly debated.
Summary Thermogenic supplements boost metabolism, increase fat burning and reduce appetite. They’re available without a prescription and can contain just one ingredient or a blend of thermogenic compounds.
1. Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous stimulant, with mild diuretic properties, found naturally in coffee, tea, as well as many soda drinks and chocolate. It is often used by athletes as a pre-workout stimulant and appetite suppressant, and is found in many products designed to aid in fat loss. Overuse, or taking this too late in the day can affect sleep patterns and removing caffeine from a diet heavy in caffeine can frequently lead to caffeine withdrawal symptoms such as headaches. Caffeine enhances the contractility of skeletal and cardiac muscle, and helps metabolise fat, thereby sparing muscle glycogen stores. Side effects can include irritability, restlessness, diarrhoea, insomnia, and anxiety
Caffeine is a stimulant naturally found in over 60 different plants, including coffee, cocoa, tea, kola nut, guarana and yerba mate (1Trusted Source, 2Trusted Source).
This stimulant also reduces appetite and boosts metabolism, helping you burn more calories while eating less (3Trusted Source).
Research has found that every milligram of caffeine consumed helps burn an additional 0.1 calories in the following 24 hours. This means that taking a 150-mg caffeine pill would burn an additional 15 calories over the course of a day (4Trusted Source).
Human and animal studies show that doses of 1.4–2.3 mg of caffeine per pound (3–5 mg per kg) of body weight are most effective in boosting metabolism and increasing fat burning (3Trusted Source).
2. Green Tea / EGCG
Green Tea is well known for its antioxidant effects. Less well known are its ability to increase thermogenesis and suppress appetite. This combination of effects makes green tea extract an increasingly popular ingredient in nutritional supplements owing to its diverse range of beneficial effects
Green tea contains two compounds that have thermogenic effects: caffeine and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source).
As noted above, caffeine stimulates the release of adrenaline, which boosts metabolism and increases fat burning. EGCG enhances these effects by slowing the breakdown of adrenaline so that its impact is amplified (6Trusted Source, 7Trusted Source).
Research has found that caffeinated green tea supplements can increase metabolism by roughly 4% and boost fat burning by 16% for 24 hours after ingestion (4Trusted Source).
One review found that overweight or obese people who consumed green tea supplements daily for at least 12 weeks lost only 0.1 pounds (0.04 kg) and reduced their waist size by just 0.1 inches (2 cm) (8Trusted Source).
However, a different review found that individuals who took green tea supplements for the same time period experienced an average weight loss of 2.9 pounds (1.3 kg), regardless of the dose taken (9Trusted Source).
3. Capsaicin
Capsaicin is the molecule that makes chili peppers spicy — the spicier the pepper, the more capsaicin it contains.
Like caffeine, capsaicin stimulates the release of adrenaline, which speeds up metabolism and causes your body to burn more calories and fat (10Trusted Source).
It also reduces appetite, making you eat fewer calories. Together, these effects make capsaicin a powerful thermogenic substance (11Trusted Source).
A review of 20 studies found that capsaicin supplements can boost metabolism by about 50 calories per day, which could lead to significant weight loss over time (12Trusted Source).
Another study showed that dieters taking 2.5 mg of capsaicin with each meal burned 10% more fat in the subsequent 24 hours, compared to a control group (13Trusted Source).
Supplementing with 6 mg of capsaicin daily has also been linked to reductions in belly fat over a three-month period (14Trusted Source)
However, there is some evidence that your body can adapt to capsaicin, reducing these effects over time (15Trusted Source).
4. Garcinia Cambogia
Garcinia cambogia is a tropical fruit whose extracts are often used in weight loss supplements.
It contains a compound called hydroxycitric acid (HCA) that can block the activity of the enzyme ATP citrate lyase, which is involved in the formation of body fat (16Trusted Source).
A review of 12 studies found that taking garcinia cambogia supplements over 2–12 weeks leads to a 1% greater reduction in body weight compared to a placebo, on average. This is a difference of roughly 2 pounds (0.9 kg) (17Trusted Source).
However, there is no consensus on garcinia cambogia’s fat impact, since other research results have been mixed (18Trusted Source, 19Trusted Source, 20Trusted Source, 21Trusted Source).
More studies are needed to understand whether garcinia cambogia supplements are effective for weight loss or reducing body fat.
5. Yohimbine
Yohimbine is a chemical derived from the bark of the African yohimbe tree, and is commonly taken as a thermogenic supplement.
It works by increasing the activity of several hormones, including adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, which could theoretically boost fat metabolism (22Trusted Source, 23Trusted Source).
The effectiveness of yohimbine for fat loss has not been researched much, but early results are promising.
One small study found that professional athletes who took 20 mg of yohimbine daily for three weeks had 2% less body fat than athletes taking a placebo (24Trusted Source).
Yohimbine may be especially effective for weight loss when combined with exercise, since it has been shown to boost fat burning during and after aerobic exercise (25Trusted Source).
At present, there is not enough research to determine whether yohimbine truly helps burn body fat.
6. Bitter Orange / Synephrine
Bitter orange, a type of citrus fruit, contains synephrine, a compound that is a natural stimulant, similar in structure to ephedrine.
While ephedrine has been banned in the United States due to reports of sudden heart-related deaths, synephrine has not been found to have the same effects and is considered safe to use in supplements (26Trusted Source).
Taking 50 mg of synephrine has been shown to increase metabolism and burn an additional 65 calories per day, which could potentially help people lose weight over time (27Trusted Source).
A review of 20 studies using bitter orange alone or in combination with other herbs found that it significantly increased metabolism and weight loss when taken daily for 6–12 weeks (28Trusted Source).
No studies have attempted to determine whether it reduces body fat in humans.
7. Thermogenic Blends
Since many substances have thermogenic effects, companies often combine several of them in one supplement, hoping for greater weight loss effects.
Studies show that these blended supplements provide an extra metabolism boost, especially when combined with exercise. However, there have not been many studies to determine whether they reduce body fat (29Trusted Source, 30Trusted Source, 31Trusted Source, 32Trusted Source).
One eight-week study found that overweight and obese dieters who took a daily supplement containing green tea extract, capsaicin and caffeine lost an additional pound (0.9 kg) of body fat, compared to a placebo. Yet, more research is needed (33Trusted Source).
Summary Popular thermogenic supplements include caffeine, green tea, capsaicin, garcinia cambogia, yohimbine and bitter orange. These substances can boost metabolism, increase fat burning and reduce appetite, but the effects are relatively small.
Thermic Effect of Fats
The thermic effect of fat depends on your body fat percentage.In lean individuals, it averages 14.4%, and ranges from 11-18%.
In obese individuals, it’s close to zero- in fact, ingesting fat, on average, decreases obese subjects metabolic rate by a fraction of a percent.
Now you might ask how it’s possible that digestion could cost negative calories.It isn’t, really.It’s just that the researchers can’t measure how many calories are spent digesting food per se, but only the overall change in metabolic rate after eating.The actual TEF of fat in obese people must be positive, but what’s happening here is that obese subjects see other parts of their metabolism slow down after eating fat- they go into a “food coma.”
This goes to show you just how badly obesity fucks up your body.You have all that excess fat, and yet your body is highly reluctant to oxidize it, preferring instead to store more and more fat.
The type of fat does make a difference- maybe even a big one.Medium-chain triglycerides, like coconut oil, have a much higher TEF than other fats, and eating them increases fat loss.Omega-3 fats, like you’d find in fish, also provide an increased TEF in men with metabolic syndrome– meaning they offset the reduced TEF from being obese.It’s not clear if they offer an increased TEF for lean individuals, but eating monounsaturated fat instead of saturated fat does improve fat loss results in overweight people.
Bear in mind, this is from consuming pure fat.Not a very fatty meal, but actually pure fat.
Thermic Effect of Carbohydrates
The thermic effect of carbohydrates depends on your insulin sensitivity, and maybe also your body fat percentage.
It’s higher in insulin sensitive people, and lower in insulin resistant people.The impact of body fat percentage is less clear.That study showed that the TEF of carbs is higher in lean people than obese people, but this study showed the reverse- it was higher in obese people.
The different findings in those two studies seem to be due to differences in methodology.Regardless, obese people are more likely to be insulin resistant, and lean people are more likely to be insulin sensitive.There’s not a one to one correlation between the two, but getting leaner will almost always improve your insulin sensitivity.
It’s also higher in high-fiber carbs.yes, celery burns a lot of calories- it just doesn’t have negative calories.
For relatively lean individuals with normal insulin sensitivity, the thermic effect of carbohydrates is around 15%- very close to the TEF of fat.
Thermic Effect of Protein
The thermic effect of protein is around 20%.Unlike fat and carbs, this seems to be very constant and unaffected by body fat percentage or insulin sensitivity, or anything else for that matter.It’s just 20%, plain and simple.
That should be considered in comparison to fat and carbs though.If you’re lean and insulin sensitive, that’s 20% vs 15%- a nice but modest increase.
If you’re obese and insulin resistant, though?That 20% looks amazing compared to the roughly 0% TEF of fat, or the 5-10% TEF of starches and sugars.Bro bodybuilders tend to eat more protein than they really need, but obese people could benefit tremendously from a high-protein diet.
We’re not done yet though.
Thermic Effect of Mixed Meals
So far we’ve looked at each macronutrient in isolation, but what happens when you mix significant amounts of all three of them in a single meal?
Simply put, it’s way better.Logically, you’d think a mixed meal would be a the weighted average of it’s components, but in this case the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.The TEF of mixed meals is around 13% in obese subjects and 25% in lean ones.
That begs the question- what constitutes a mixed meal?Do you need to have a totally even mix of macronutrients, or just a certain minimum amount of each, and there are diminishing returns beyond that?Right now we don’t have enough data to answer that.
Here are my best-guess general guidelines:
Protein: at least 25% of the calories in each meal if you’re lean, and 40% if you’re obese
Fat: at least 20% of the calories in each meal
Carbs: at least 20% of the calories in each meal. If you’re on a ketogenic diet, you obviously can’t go that high, but try to include like 5-10 grams of carbs with every meal to boost the TEF.
The Negative Effect of Food Processing
Processed foods have a much lower TEF than unprocessed foods. It can be nearly a two-fold difference, in fact– whole wheat bread with cheddar has a TEF of around 20%, vs 11% for white bread and processed cheese.
Processing food simply make food so much worse as it takes away a hug amount of the digest and nutritious requirements and therefore is almost 100 for 100 when it comes to calorie count.
The Final Word: Eat Unprocessed, Mixed Meals, and Be Lean
In practice, the TEF of mixed meals can be anywhere from ten to thirty percent.In practice, it’s usually 10-15% if your diet is unhealthy (but still somewhat balanced and consisting of mixed meals), and 20-25% if you eat a truly healthy diet.
Based on my synthesis of the research and a little educated guesswork, here are some general guidelines for estimating TEF based on what you’re eating and how lean you are.
|
Meal Type |
Obese |
Average |
Lean |
|
Almost pure protein (chicken breast) |
18% |
19% |
20% |
|
Almost pure fat (nuts, really fatty bacon) |
0 |
10% |
14% |
|
Almost pure carbs (fruit, crackers, low-fat chips) |
5% |
10% |
14% |
|
Low-protein, processed mixed meal (grilled cheese sandwich) |
10% |
11% |
12% |
|
High-protein, processed mixed meal (roast beef sandwich) |
15% |
16% |
20% |
|
Low-protein, unprocessed mixed meal (chicken salad) |
15% |
21% |
23% |
|
High-protein, unprocessed mixed meal (chicken, mixed vegetables and beans) |
20% |
24% |
25% |
|
High-protein, unprocessed mixed meal with MCT or n-3 fats and high fiber (salmon, potato and mixed vegetables) |
23% |
26% |
27% |
As you can see, being obese hurts you a lot, and you have to make up for it by eating at a big deficit to begin with, and eating extra clean.Eating unprocessed food is always important, while eating high protein is important if you’re obese and less so as you get leaner.
The need to eat mixed meals is yet another reason not to snack between meals- since snacks usually consist of just one food item, they’re not mixed meals.
The good news is, there’s no particular food you need to eat to maximize TEF. Adding some MCT or omega-3 fats with every meal helps a little bit, but the main thing is to eat unprocessed mixed meals with a decent amount of protein.As long as you do that, you can be very flexible about what you eat while still benefiting from a high thermic effect of food.